“Reported rates of sexual assault in the military have increased dramatically over the past 10 years (Groves, 2013). One reason for the pervasiveness of sexual assault is the reporting structure. Despite changes in the way sexual assault complaints are handled, there continue to be numerous sexual assault scandals (Childress, 2013). The purpose of this study is to examine how the military’s chain of command influences the reporting procedures, and how this may influence the military’s ability to prevent sexual assaults. This thesis examines three case studies specifically focusing on military sexual assault reporting.”
Lindsay Rosenthal & Lawrence Korb, Center for American Progress, Twice Betrayed Bringing Justice to the U.S. Military’s Sexual Assault Problem (2013)
“This report discusses what is known about sexual assault in the military and outlines key reform goals to combat the problem. We argue that removing cases from the chain of command is a necessary step that the military must take to address military sexual assault. Taking the decision to prosecute assault cases out of the chain of command is critical to reduce sexual violence and hold sexual predators in the armed forces accountable. We discuss changes that need to be made, including increasing accountability for perpetrators and military leadership, improving victim services, increasing reporting of sex crimes to military authorities, and improving data collection and transparency related to sexual assault in the armed forces.”
David Cantor et al., AAUW/Westat, Report on the AAU Campus Climate Survey on Sexual Assault and Sexual Misconduct (Oct. 20, 2017)
“Members of the Association of American Universities (AAU) are working to combat sexual assault and misconduct on their campuses. As an association of research universities, AAU decided in 2014 that the best way to help its members address this issue was to develop and implement a scientific survey to better understand the attitudes and experiences of their students with respect to sexual assault and sexual misconduct. The survey’s primary goal was to provide participating institutions of higher education (IHEs) with information to inform their policies to prevent and respond to sexual assault and misconduct. In addition, members hoped that the survey would provide useful information to policymakers as well as make a significant contribution to the body of academic research on this complex issue.”
Nick Anderson & Scott Clement, 1 in 5 College Women Say They Were Violated, Wash. Post (June 12, 2015)
“The Washington Post and the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation teamed up to poll more than 1,000 people nationwide who have attended college within the past four years about sexual assault and campus culture. Post reporters then interviewed more than 50 women and men who responded that they had experienced unwanted sexual contact — or attempted or suspected sexual contact — while they were students. The series looks at the prevalence of sexual assault among college students and the factors that play a role in those assaults.”
Bianca DiJulio et al., Survey of current and Recent College Students on Sexual Assault, KFF Polling (June 12, 2015)
“This partnership poll from The Washington Post and the Kaiser Family Foundation examines the issue of sexual assault on college campuses by exploring the views and experiences of students ages 17 to 26 currently or recently enrolled in a four-year college or university who live on or near campus. The survey, one of the most comprehensive to date on the issue, explores students’ views of consent, effective prevention strategies, and school administrations’ handling of incidents, as well as provides new, nationally representative estimates of the share who say they were sexually assaulted during college.”
Charol Shakeshaft, U.S. Dept. of Educ., Educator Sexual Misconduct: A Synthesis of Existing Literature (2004)
“Any adult misconduct or sexual abuse in schools is of grave concern to students, parents, educators, and the Department of Education. This literature review of sexual abuse and sexual misconduct responds to the mandate in Section 5414 of the Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965 (ESEA), as amended, to conduct a study of sexual abuse in U.S. schools. To satisfy this mandate, the Department of Education contracted with Dr. Charol Shakeshaft of Hofstra University. Using the limited research that is available in this area, her literature review describes, among other topics: prevalence of educator sexual misconduct, offender characteristics, targets of educator sexual misconduct, and recommendations for prevention of educator sexual misconduct. We note that the author offers several new recommendations that may be worth considering, although some may be at odds with current law.”
Kevin Miller, Schools Are Still Underreporting Sexual Harassment and Assault, AAUW Education and Training (Nov. 2, 2018)
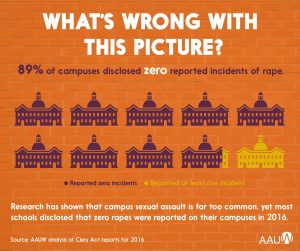
“Students should be able to go to school free from experiencing sexual harassment or violence. That’s the promise made over 45 years ago by Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972, which prohibited sex discrimination in any educational institution or program receiving federal funding.
Unfortunately, despite Title IX’s best efforts, and the additional protections afforded to students by the federal Clery Act and other state and local laws, sexual harassment and violence still interfere with the education of too many students. Even more alarming is that many schools make it difficult for students to come forward and that schools fail to properly report incidents of sexual harassment and violence when they occur. As a result, many students remain negatively impacted by unlawful sex discrimination in schools.”
Nan Stein, Sexual Harassment in School: The Public Performance of Gendered Violence, 65 Harv. Ed. Rev. 145 (1995)
“In this article, Nan Stein argues that sexual harassment in schools is a form of gendered violence that often happens in the public arena. She presents the narratives of girls and boys about their experience of sexual harassment in schools and finds parallels with cases documented in court records and depositions. While highly publicized lawsuits and civil rights cases may have increased public awareness of the issue, inconsistent findings have sent educators mixed messages about ways of dealing with peer-to-peer sexual harassment. The antecedents of harassment, she suggest, are found in teasing and bullying, behaviors tacitly accepted by parents and teachers. Stein makes a case for deliberate adult intervention and the inclusion of a curriculum in schools that builds awareness of these issues.”
Campbell Leaper & Christia Spears Brown, Perceived Experiences with Sexism Among Adolescent Girls, 79 Child Dev. 685 (2008)
“This study investigated predictors of adolescent girls’ experiences with sexism and feminism. Girls (N = 600; M = 15.1 years, range = 12-18), of varied socioeconomic and ethnic backgrounds, completed surveys of personal experiences with sexual harassment, academic sexism (regarding science, math, and computer technology), and athletics. Most girls reported sexual harassment (90%), academic sexism (52%), and athletic sexism (76%) at least once, with likelihood increasing with age. Socialization influences and individual factors, however, influenced likelihood of all three forms of sexism. Specifically, learning about feminism and gender-conformity pressures were linked to higher perceptions of sexism. Furthermore, girls’ social gender identity (i.e., perceived gender typicality and gender-role contentedness) and gender-egalitarian attitudes were related to perceived sexism.”
Jennifer Ann Drobac, Sexual Exploitation of Teenagers: Adolescent Development, Discrimination & Consent Law

“In Sexual Exploitation of Teenagers, Jennifer Drobac explores the shockingly common problem of maturing adolescents who are harassed and exploited by adults in their lives. Reviewing the neuroscience and psychosocial evidence of adolescent development, she explains why teens are so vulnerable to adult harassers. Even today, in an age of increasing public awareness, criminal and civil law regarding the sexual abuse of minors remains tragically inept and irregular from state to state. Drobac uses six recent cases of teens suffering sexual harassment to illuminate the flaws and contradictions of this system, skillfully showing how our current laws fail to protect youths, and offering an array of imaginative legal reforms that could achieve increased justice for adolescent victims of sexual coercion.”
